- Usage
- Usage Cases
- Diabetes mellitus,diabetic foot
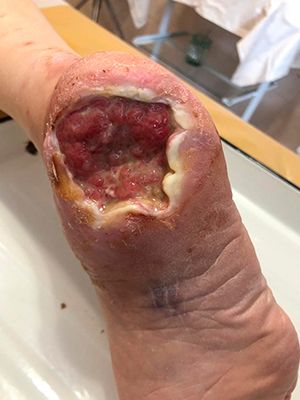
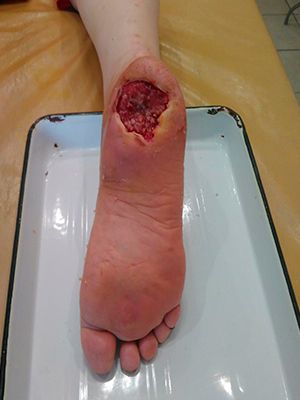
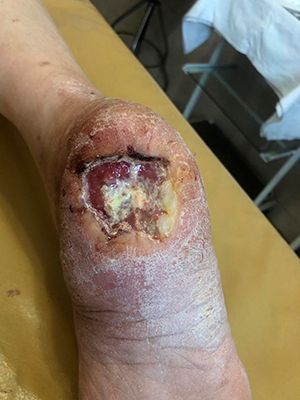
Case №45
Diabetes mellitus,diabetic foot
Application of Mirragen: 30.09.2019
National Institute of Surgery and Transplantology named after Shalimov. Kiev.
-
Patient:
Woman
-
Age:
60 years old
-
Diagnosis:
Diabetes mellitus,diabetic foot
Clinical presentation and diagnosis of SDS
In the early stages, patients complain of leg fatigue, chilliness, paresthesia, which fits into the clinical picture of the formation of diabetic polyneuropathy. The persistence and severity of these complaints depend on the stage of the disease. Annual examination of the feet by a specialist is the minimum and necessary requirement for monitoring patients with diabetes, which is performed in all patients with diabetes, regardless of the age of the diagnosis.
When examining a patient with SDS, one should pay attention to the color of the extremities, the presence of edema, deformity of the foot, the presence of pathological mobility in the joints, the localization of the ulcer, the nature of the discharge, the undermining of the edges, the condition of the surrounding skin (eczema, induration). According to international experts and the results of scientific research. conducted at the Center "Diabetic Foot", for screening patients with neuropathy who are at risk, the following methods are recommended: a blunt needle injection on the back of the thumb, monofilament 10 g, tuning fork.
The patient is at risk of developing SDS if he does not feel the touch of the monofilament at more than one point, or does not feel pain when the dorsum of the thumb is pricked, or vibration sensitivity according to the readings of a tuning fork Ј 3 c.u. ...
The simplest way to assess OPS is considered to be the measurement of the angle of dorsiflexion of the 1st finger, performed by a goniometer or goniometer. Due to a change in temperature, tactile, proprioceptive sensitivity, microtraumas are frequent (treatment of corns, foreign bodies in shoes, tight shoes, thermal procedures), the spontaneous healing of which does not occur, phlegmon, trophic ulcers, and gangrene of the feet develop. Mycotic injuries of the feet as a result of atrophy and deformation of the nail plate are common.
Intermittent claudication syndrome is a sign of the ischemic form of SDS. Special research methods are aimed at identifying lesions of the arteries of the extremities. These are radiopaque arteriography, Doppler study of arterial blood flow, computer video capillaroscopy. To assess the condition of the wound, cytological and bacteriological studies of ulcers are necessary.
According to the recommendations of the International Working Group (2011) on the diabetic foot, differentiated approaches for diagnosis and treatment have been determined depending on the types of limb lesions.
Of the imaging methods, MRI is the most informative. CT and radioisotope imaging are less reliable. Conventional radiography is widely used. The main causes of severe intoxication are gangrene, necrotizing fasciitis, and deep tissue abscess. In these situations, urgent surgical intervention is required, the timely implementation of which reduces the risk of high amputation. Some patients with osteomyelitis can be successfully treated with antibiotic therapy without surgical removal of the affected bone. Antibiotic therapy is required only in patients with clinical signs of infection.
Local wound treatment
Despite the large number of products for local wound treatment (dressings, ointments, etc.), the effectiveness of the vast majority of them has not been confirmed. There is no doubt about the benefits of the following components of treatment:
- Regular rinsing with a stream of water or saline reduces the number of bacteria on the surface of the wound;
- a dressing that absorbs excess exudate, but does not allow the wound to dry out (forming a moist environment);
- Regular necrectomy and removal of hyperkeratosis with a scalpel.
- An innovative method of treating trophic ulcers in osteomyelitis and diabetic foot is the application of the Mirragen Product topically to restore the wound surface
Immediately after entering the damaged cavity, bioactive fibers react with natural exudate and promote the release of active electrolytes into the wound, which leads to an acceleration of the healing process by about 40% compared to the use of other means.
Cooperate With Us
or via contact phones or email
-
Conveniently
By contacting only one supplier, our customers receive a wide range of products in the shortest possible time.
-
Simple
Our customers are only required to form an order for the supply of products, we will take care of all further tasks
-
Profitable
We save our customers money on import
and delivery taxes