- Usage
- Usage Cases
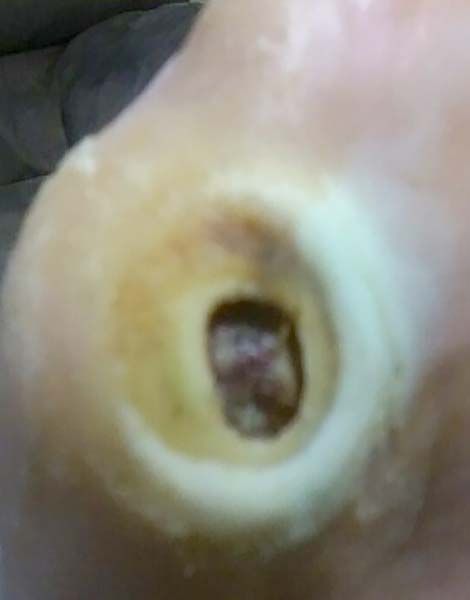
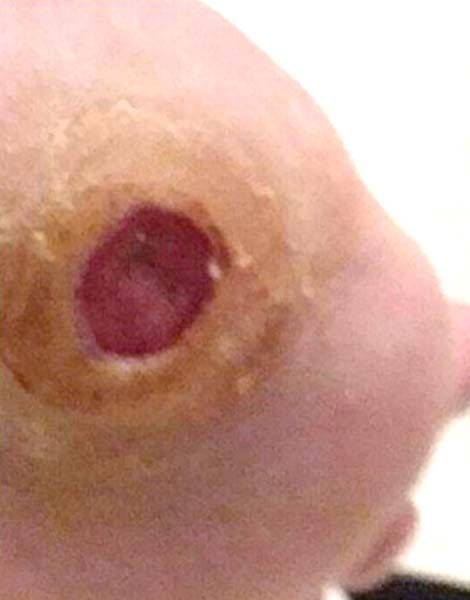
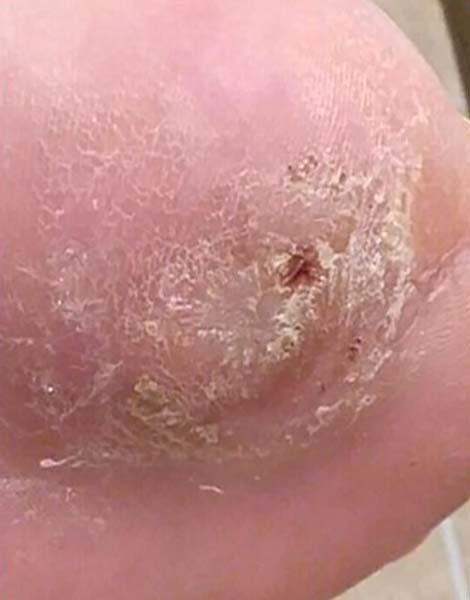
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Case №25
Diagnosis: Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Age of Wound: 1 year
-
Gender:Man
-
Age:80 years
-
Diagnosis:Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Diabetic foot treatment
Treatment of diabetic foot begins with an analysis of the causes of the disease. Diabetic foot syndrome is a condition that develops in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition in which the pancreas does not produce enough insulin (type 1 diabetes) or when the body develops a tolerance for its own insulin, which leads to ineffective use of it (type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a pancreatic hormone whose ultimate effect is to lower blood glucose levels by transferring it to cells for energy.
It is determined by a set of clinical, laboratory and instrumental signs of impaired blood flow, as well as innervation of the distal parts of the lower extremities. It is characterized by the development of ulcerative-necrotic processes in soft tissues, destruction of the osteoarticular apparatus and impaired support function of the foot, which leads to a decrease in the quality of life and, in case of untimely treatment, disability of the patient.
Forms of lesions of the diabetic foot
-
With a predominant lesion of peripheral nerves, one should talk about the neuropathic form of the diabetic foot. Patients will more often complain of neuropathic pain in the feet (often diminishing with walking), impaired sensitivity in the feet (hypo-, hyper- and paraesthesia), dense swelling of the feet. In the future, with untimely treatment, uncontrolled course of diabetes mellitus, patients may develop complications of the diabetic foot: trophic ulcers, which more often occur in places of increased pressure when walking (plantar surface of the thumb, projections of the metatarsal heads, heel area); the development of purulent-necrotic complications with the attachment of pathogenic flora in the form of wet gangrene of fingers and feet.
-
In case of damage to peripheral vessels, the ischemic form is isolated. Patients note pain in the feet, which increases when walking and can be reduced by lowering the limb, coldness and paleness of the feet, rapid fatigue in the feet (they can take breaks when walking at a distance of more than 500-1000 m).
-
In the absence of control and adequate treatment, trophic ulcers can develop (more often located on the dorsum of the fingers, the back of the foot), as well as dry gangrene of the phalanges of the fingers and toes.
-
Mixed form, which includes the totality of symptoms of both forms. As a rule, a mixed form prevails in clinical practice, since the processes of damage to nerves and blood vessels in the diabetic foot proceed in parallel in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Diabetic foot treatment by different specialists
-
Endocrinologist - ensures glycemic control by adjusting the doses of oral tablet preparations and insulin therapy.
-
Neuropathologist - corrects neurotropic therapy, evaluates the quality of subjective and objective changes in the sensitivity of the foot (tactile, cold, pain sensitivity).
-
Vascular surgeon - assesses the state of ischemia in the limb, prescribes additional examinations according to indications (Doppler ultrasound of the arteries, veins of the lower extremities, CT angiography of the lower extremities), corrects therapy based on the data obtained, establishes indications for surgical treatment (different options for angioplasty, shunting).
-
Cardiologist - assesses the degree of ischemia of the heart muscle, corrects the therapy of concomitant pathology and conditions (hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, coronary artery disease).
-
Traumatologist-orthopedist - evaluates the degree of foot deformity, corrects and prescribes osteotropic therapy, helps in the selection of prostheses for amputations of the foot and lower leg.
Treatment stages
-
General clinical studies - collection of complaints, anamnesis, objective examination, the patient is recruited general clinical laboratory tests, in addition - lipid profile, glycosylated hemoglobin.
-
Inspection of the feet for the presence of wound defects, areas of loss of sensitivity and areas with a reduced temperature. Palpation determination of the pulsation of the peripheral arteries of the lower extremities with a comparative assessment on each of the legs (TAS, PBBA, ZBBA, PCA, PBA, OBA). Assessment of the degree of loss of sensitivity, marking these zones Assessment of the degree of deformity of the toes, tarsal region.
-
In the presence of skin defects on the foot - their assessment on multidisciplinary scales (Wagner, PEDIS) with further determination of the tactics of local treatment.
-
Purpose of additional studies - Doppler ultrasonography of the arteries of the lower extremities (MSCT in angiography mode, if necessary), foot radiography (MSCT of the feet), electroneuromyography according to indications.
-
Appointment of consultations of related specialists for the correction of treatment tactics.
Cooperate With Us
or via contact phones or email
-
Conveniently
By contacting only one supplier, our customers receive a wide range of products in the shortest possible time.
-
Simple
Our customers are only required to form an order for the supply of products, we will take care of all further tasks
-
Profitable
We save our customers money on import
and delivery taxes