- Usage
- Usage Cases
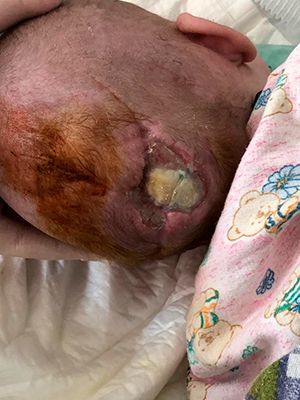
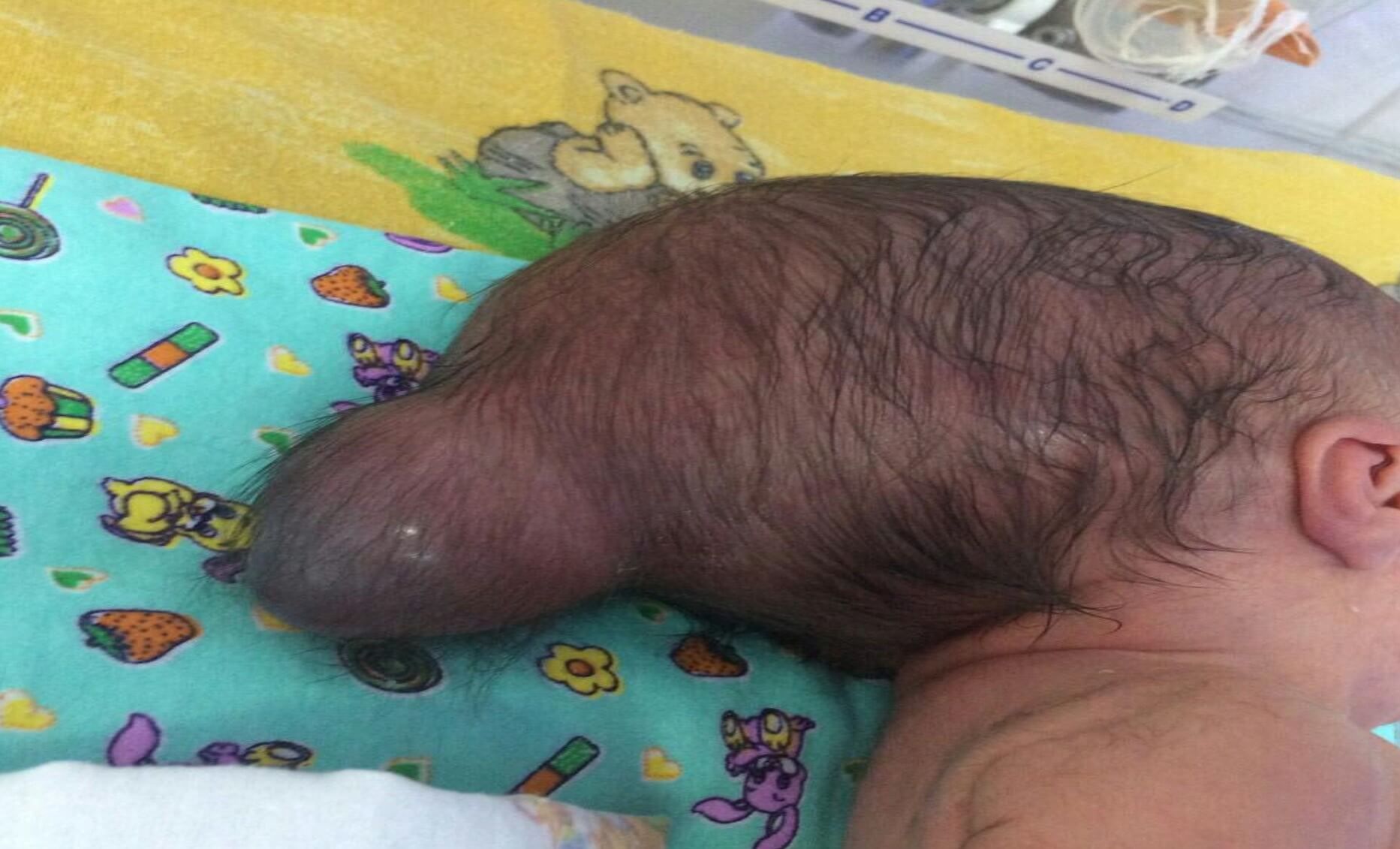
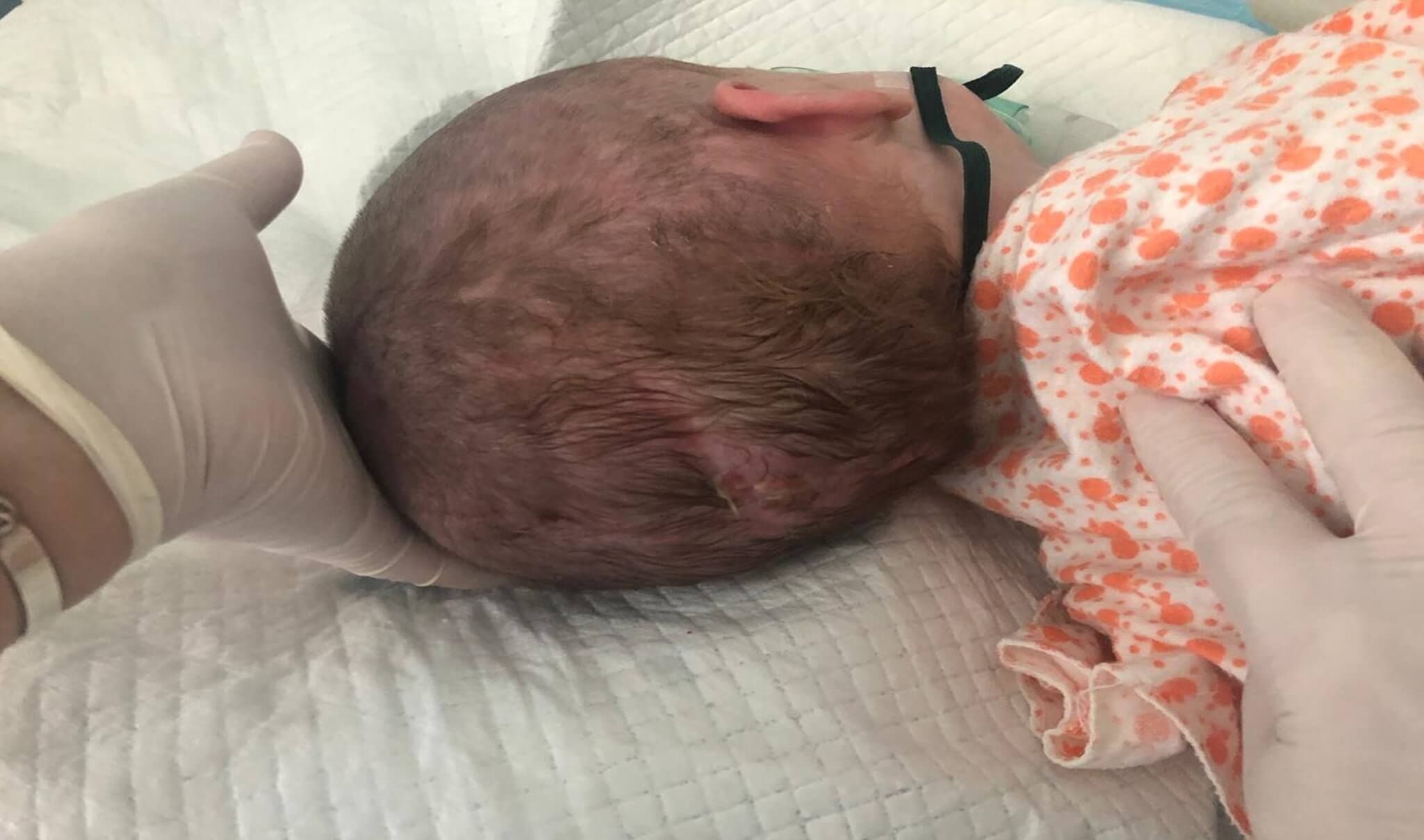
- VPR CNS posterior cerebral hernia. Internal hydrocephalus
Case №39
VPR CNS posterior cerebral hernia. Internal hydrocephalus
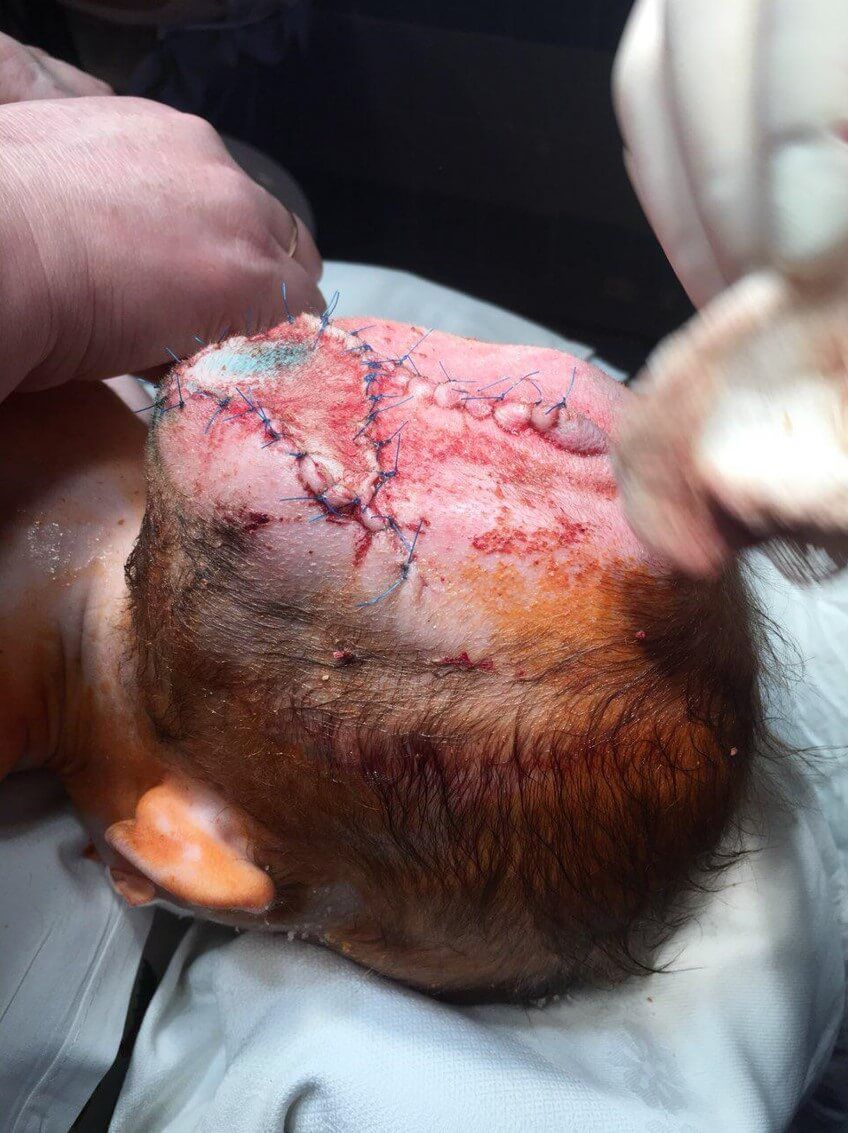
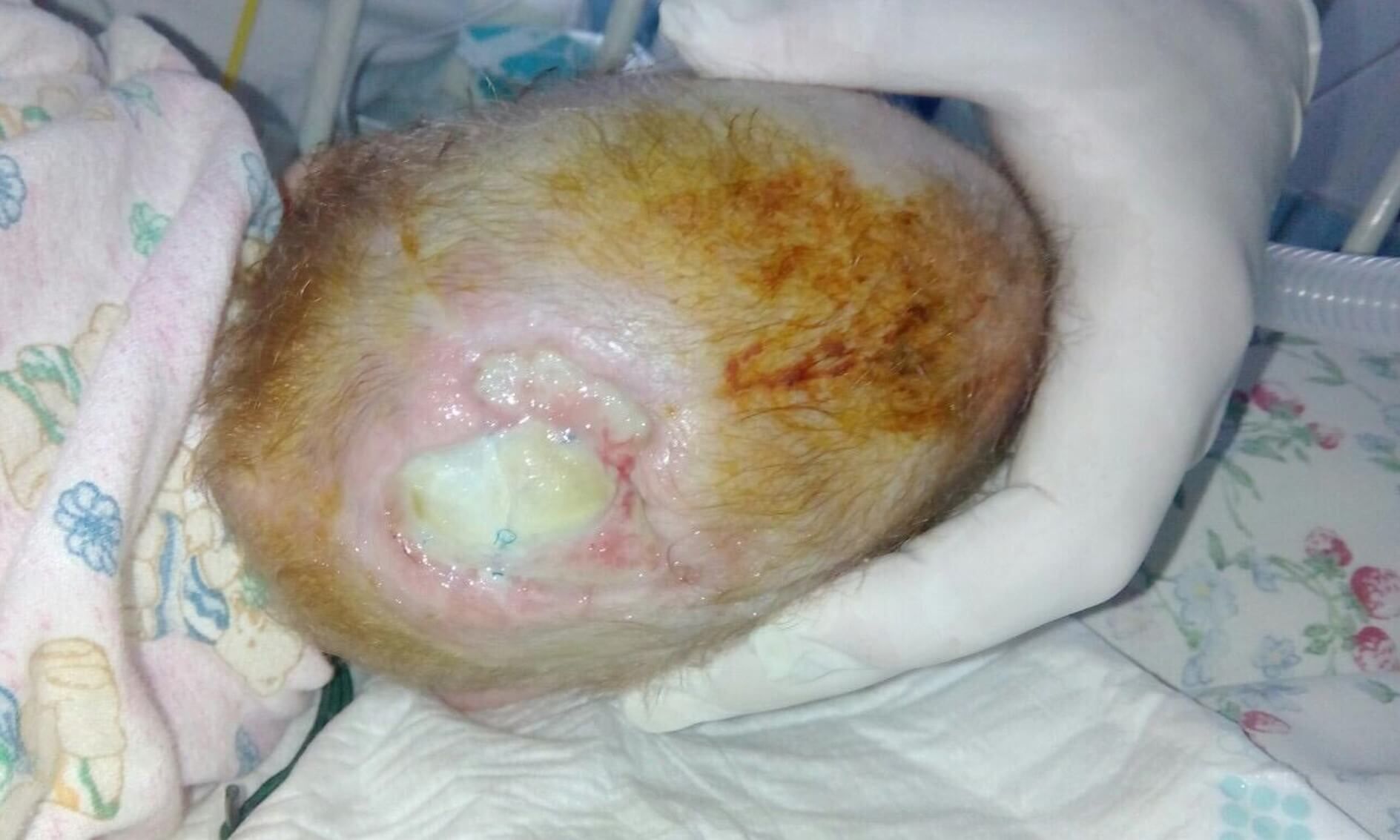
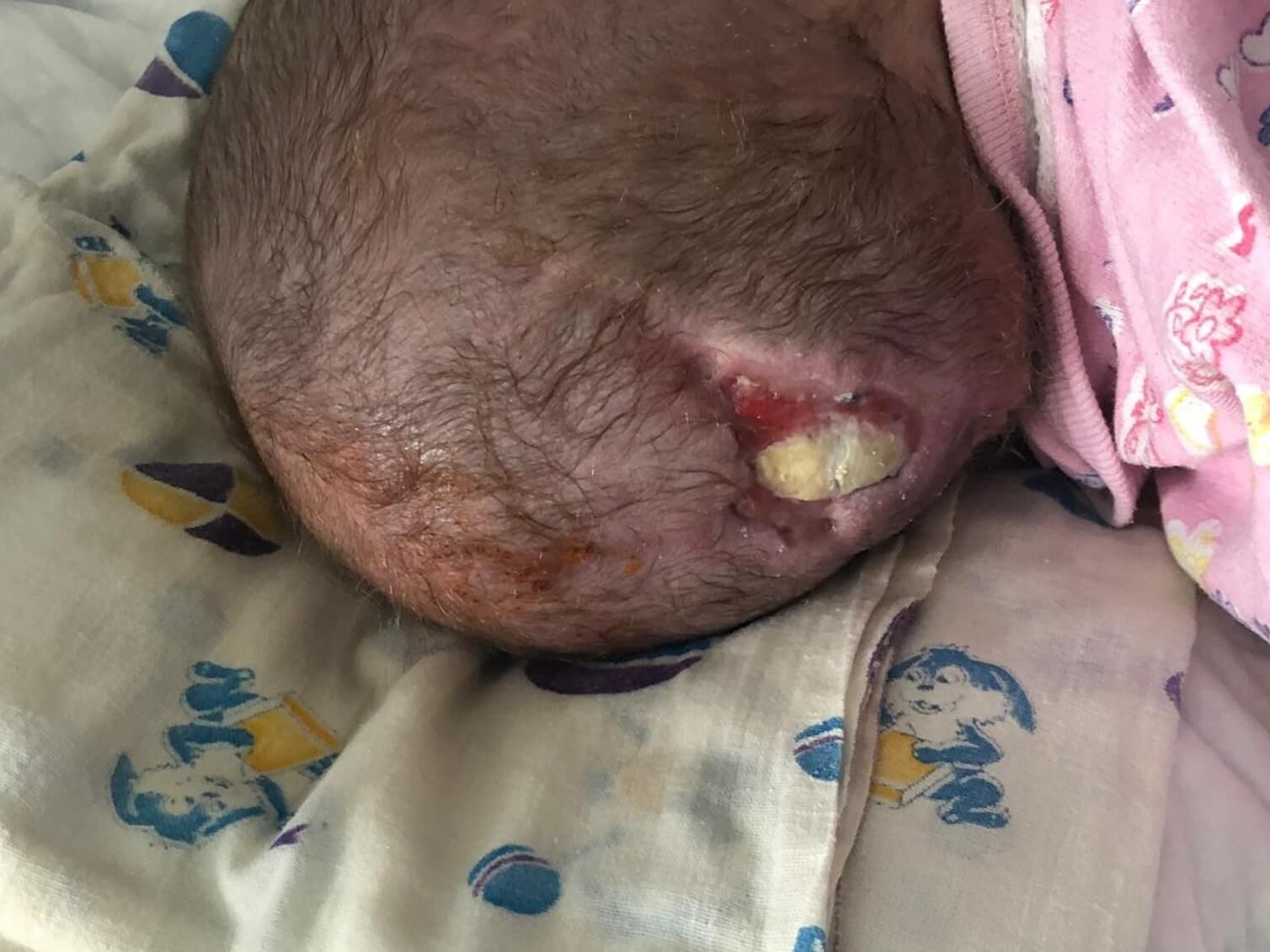
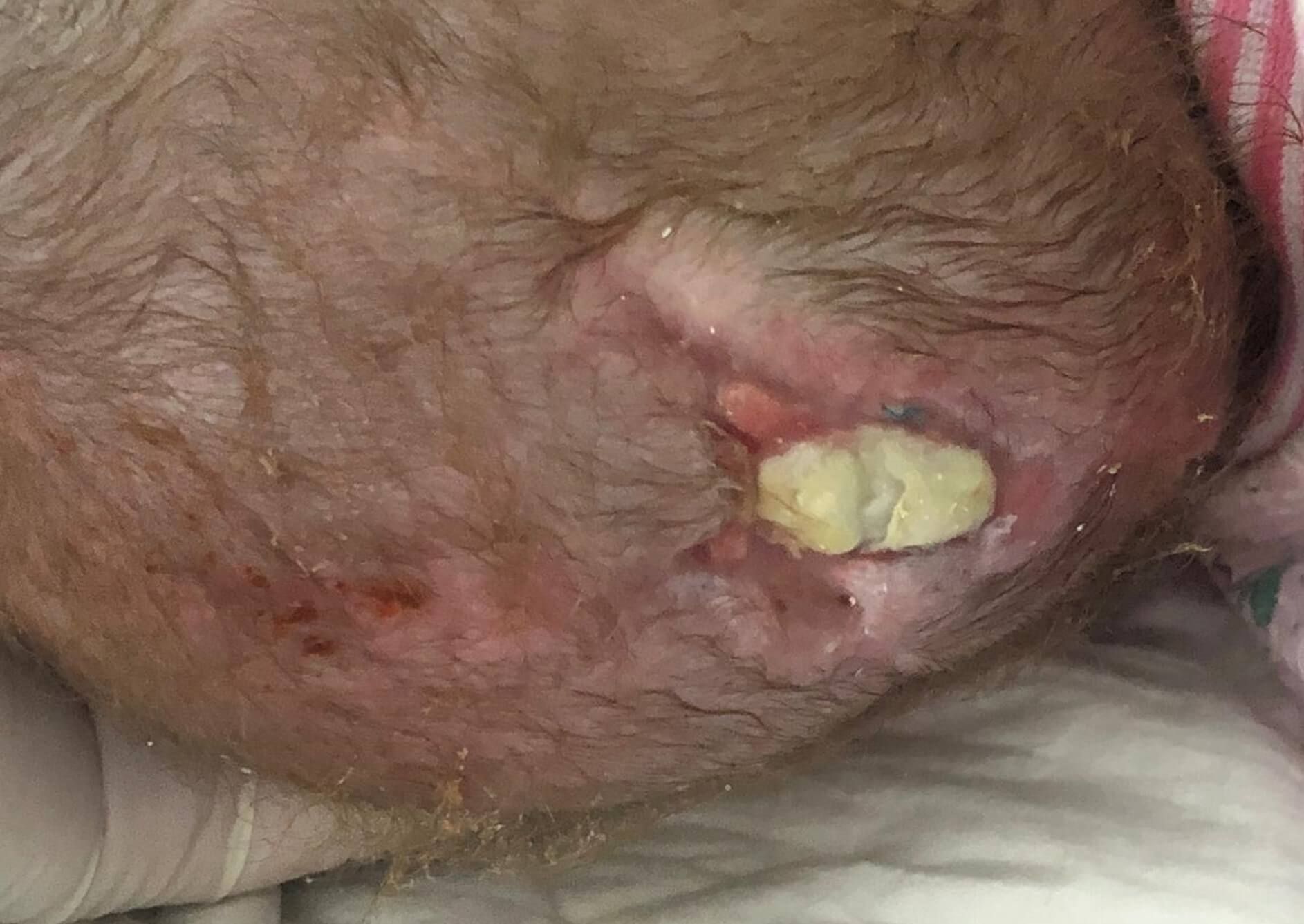
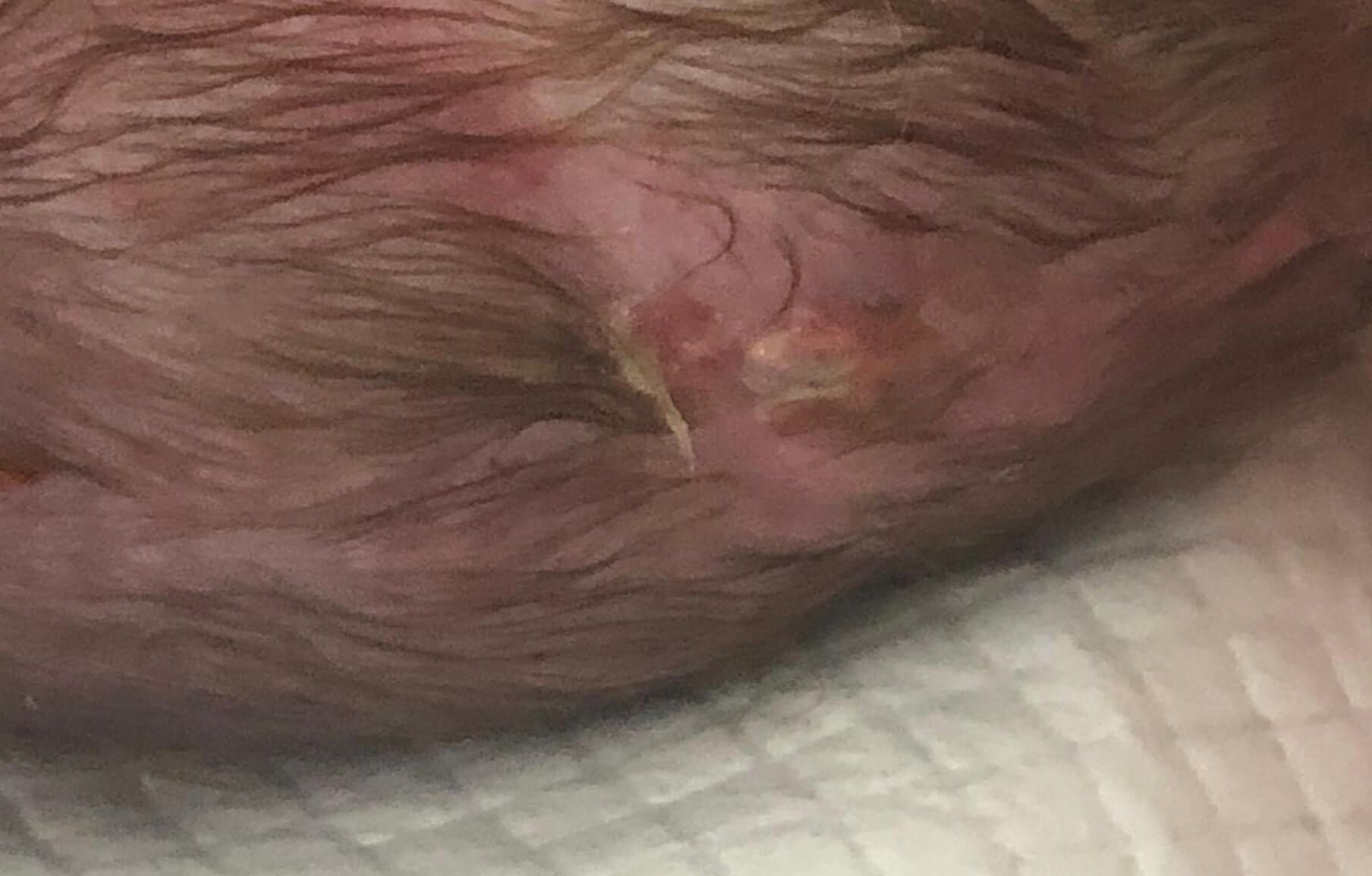
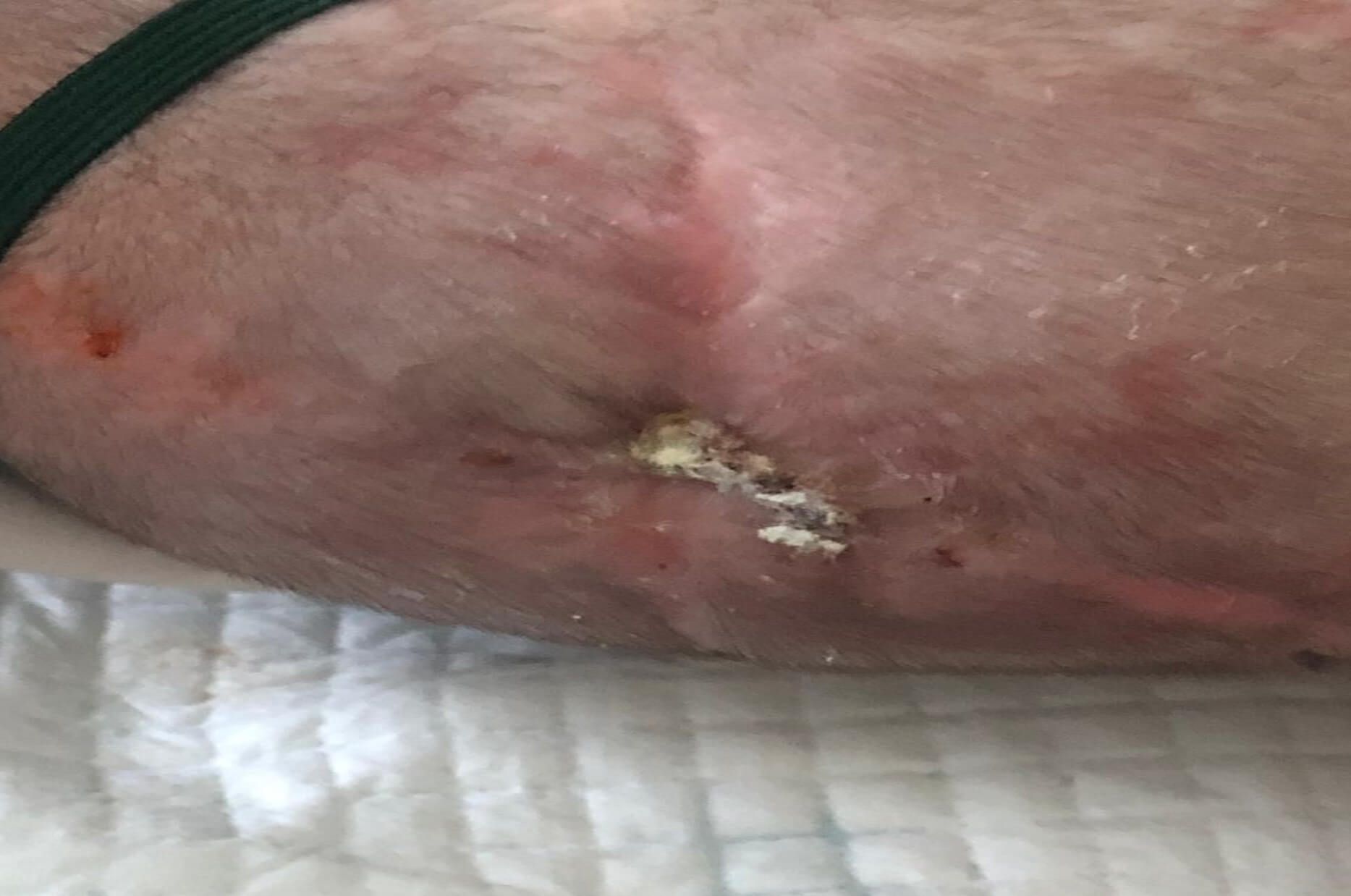
Time period for the presence of a wound : 6 months.
Application of Mirragen: 03.04.19
Odessa Regional Children's Clinical Hospital
-
Patient:
Girl
-
Age:
6 months
-
Diagnosis:
VPR CNS posterior cerebral hernia. Internal hydrocephalus
Encephalocele (cerebral hernia)
Encephalocele is a bulge of nerve tissue and meninges through a defect in the skull.
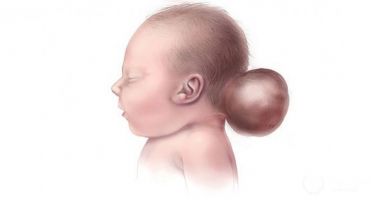
Encephalocele is caused by incomplete closure of the cranial vault (cranium bifidum).
Encephalocele classification
In medicine, four types of cerebral hernias are distinguished, depending on the location of the encephalocele:
- Hernial formation in the fornix of the skull;
- Basal hernia - no symptoms;
- Frontal, ethmoidal formation;
- Occipital hernia is the most common type.
Encephalocele usually occurs in the midline and protrudes anywhere along the line from the occiput to the nasal passages, but may be present asymmetrically in the frontal or parietal regions. Small encephalocele may resemble a cephalohematoma, but x-rays show bone defects in the skull at its base. Hydrocephalus often develops with encephalocele. About 50% of sick babies have other congenital anomalies. Symptoms and signs of encephalocele include visible defects, seizures, and altered consciousness, including impaired intellectual and motor development.
The prognosis depends on the location and size of the lesion. Most of the encephalocele can be restored. Even large lesions often contain mostly heterotopic neural tissue that can be removed without impairing the patient's functional capacity. With the combined identification of other serious deformities, the decision on the patient's neurosurgical treatment may be negative, and the prognosis of the child's development may be unfavorable.Hydrocephalus (dropsy of the brain) is a disease due to which cerebrospinal fluid accumulates excessively in the cerebrospinal fluid pathways of the brain, due to its increased production, impaired circulation or resorption. In its usual form, the disease is characterized by excess fluid in the head, which causes high pressure inside the skull.
Pathological changes are represented by the expansion of the cavities of the ventricles, flattening of the convolutions, smoothing of the furrows, atrophy of the vascular plexuses, edema, fibrosis, fusion of the meninges.Previously, hydrocephalus was an incurable disease, most often people died when they got sick, but huge advances in diagnosis and treatment methods have significantly improved the functioning of patients with hydrocephalus. In some cases, when optimal treatment is provided on time, patients can continue to lead a healthy lifestyle.
One in 1000 children born suffers from hydrocephalus. This disease is more common in premature babies born before 30 weeks. There is no difference in the prevalence of disease between boys and girls.
In most cases, the disease is associated with congenital malformations, but hydrocephalus can also be caused by infection (for example, meningitis), cerebral hemorrhage, tumors, after severe head injuries, and complications from other diseases (for example, spina bifida), so hydrocephalus can develop into any age.
How is hydrocephalus diagnosed?
If the doctor recognizes the above symptoms, the disease can be diagnosed using one of the following imaging methods: ultrasound of the child's head, computed tomography, MRI.
Treatment for Hydrocephalus is in the hands of a neurosurgeon.
The operation is carried out in two stages. First, the bone defect is closed and the hernia leg is cut off. At an early age, the opening in the skull can be closed with a periosteal flap; in later operations (over 3 years of age), a bone graft is used.
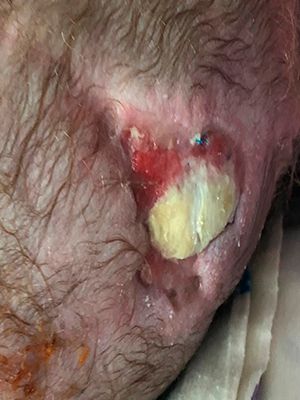
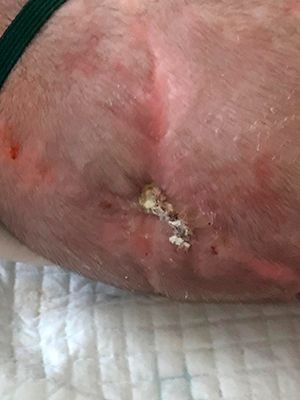
The second stage of the operation is a cosmetic excision of the superficially located remaining part of the hernial sac. It is performed 15-20 days after the first stage (3-6 months in case of intracranial access). The tactics of the operation in each case is determined depending on the degree of involvement of brain tissues in encephalocele.To restore the missing tissue, the product Mirragen is used, which contributes to the rapid and effective healing of the wound surface during these surgical interventions.
Chronology of treatment
Cooperate With Us
or via contact phones or email
-
Conveniently
By contacting only one supplier, our customers receive a wide range of products in the shortest possible time.
-
Simple
Our customers are only required to form an order for the supply of products, we will take care of all further tasks
-
Profitable
We save our customers money on import
and delivery taxes